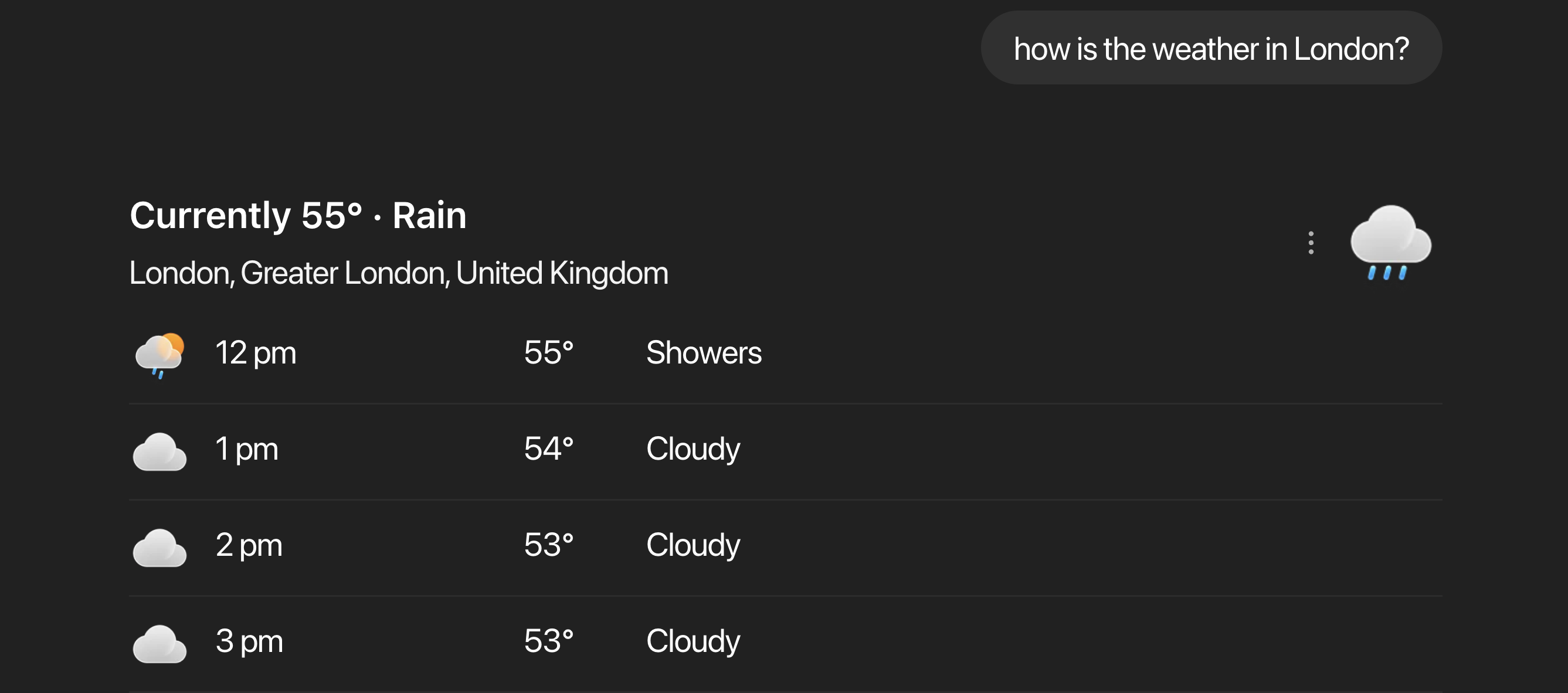
Weather Agent Example
ChatGPT accesses weather using an external API.
What is an LLM Tool?
When we say “tool”, we mean a function that can be called by an LLM to perform a task or action. But how does an LLM know how to call a tool?Tool calling with OpenAI API
LLMs first need to know the details of the tool to call it. This is done by providing a to the LLM. In the following example, we define a tool schema for a weather API function that retrieves the current weather for a given location.Tool calling flow
The following diagram illustrates the complete flow of tool calling with an LLM:MCP (Model Context Protocol) Server
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a standardized way for LLM applications to interact with external data sources and functionality. MCP servers expose capabilities through three main abstractions: Tools, Resources, and Prompts. Let’s understand the “why” behind MCP with a comparison between using MCP and not using MCP.| Without MCP | MCP |
|---|---|
| Developers need to implement the tool calling logic in the application. | A prebuilt MCP Server can be plugged into the LLM to provide tools and APIs. |
| Developers need to implement integration logic for all external tools such as weather API, email API, etc. | Think of MCP like a USB-C port for AI applications. |
Key concepts
- MCP Host: The AI application that coordinates and manages one or more MCP clients
- MCP Client: A component that maintains a connection to an MCP server and obtains context from the MCP server for the MCP host to use
- MCP Server: A program that provides context to MCP clients
Architecture
MCP follows a client-server architecture where MCP Clients (within the MCP Host) connect to MCP Servers in a one-to-one relationship. Each client maintains its own dedicated connection to a specific server.Next steps
Build a custom MCP Server
Build a custom MCP Server with Agentor to connect to your own data sources.
Celesto AI MCP Hub
Connect Agent with 100+ MCP Servers with built-in security and authentication.